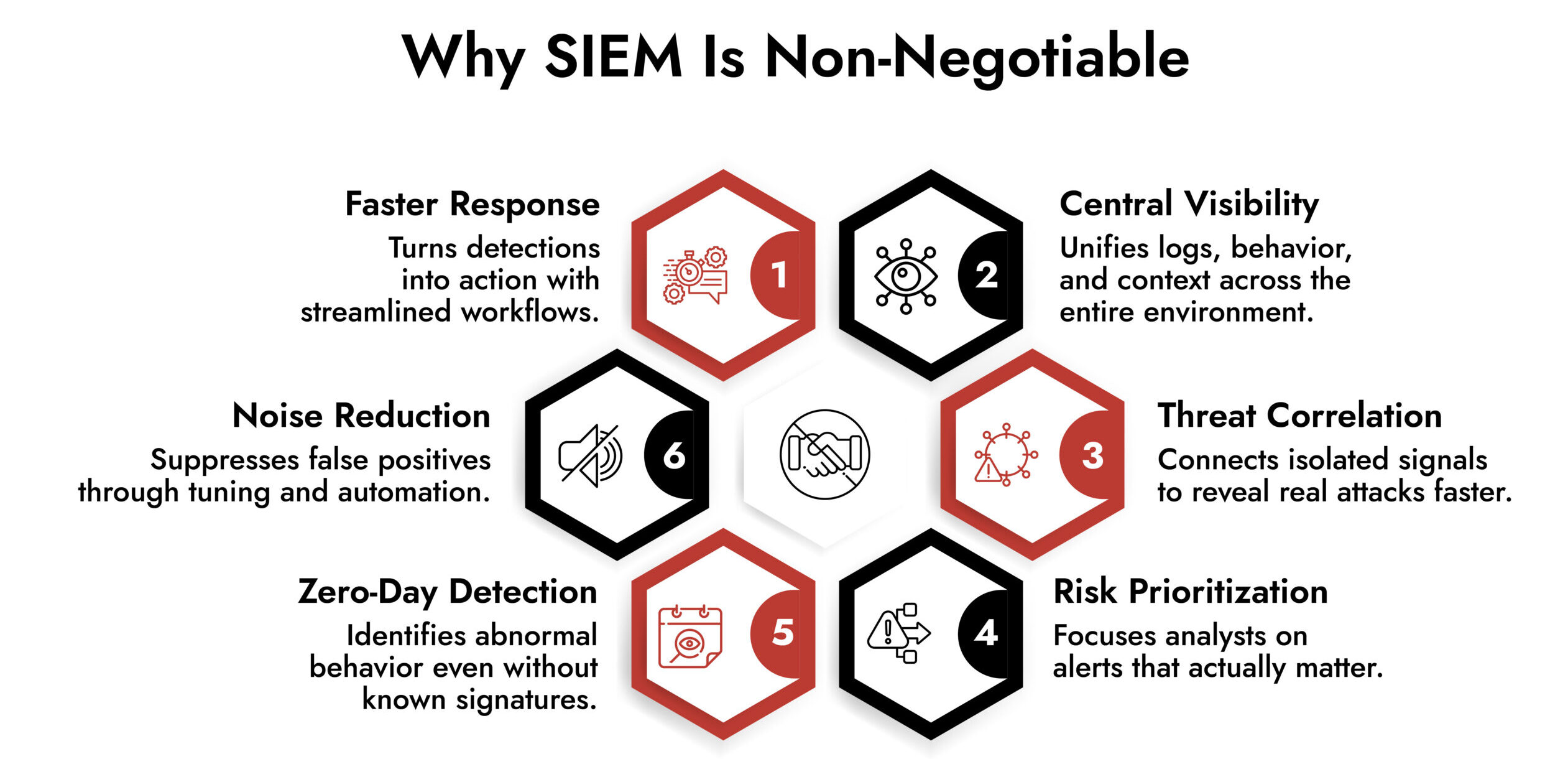
Key Takeaways
- SIEM is a detection and decision engine, not just a log collector
- Alert fatigue comes from poor configuration, not SIEM itself
- Effective SIEM deployment requires continuous tuning and use-case focus
- Risk-based prioritization is essential to reduce analyst burnout
- SIEM strengthens analysts; it does not replace them
- When aligned with business context, SIEM accelerates response and reduces risk
Most organizations believe their SIEM security is central to their detection strategy. On paper, it is. In practice, it’s often the reason response cycles stall. 83% percent of SOC analysts report being swamped by alerts they can’t contextualize, which means the system designed to elevate critical threats instead buries them. Even worse, 85% say they spend a disproportionate amount of time stitching together evidence from multiple systems just to validate whether an alert deserves attention. The disconnect isn’t technical; it’s conceptual. Teams approach SIEM with assumptions that haven’t evolved alongside the platform’s capabilities, and those assumptions silently determine which alerts get ignored, which threats go undetected, and which breaches become inevitable.
Top 8 SIEM Misconceptions
Misconception 1: SIEM Is Only Good for Collecting Logs
For many, SIEM deployment still feels like a glorified log warehouse. If all you expect from SIEM is centralized storage, compliance reporting, and long-term log retention, you will never see its full value.
A modern SIEM performs far beyond basic event collection. It:
- Correlates telemetry from endpoints, networks, identities, and cloud services
- Detects anomalies using behavioral analytics and threat intelligence
- Automates triage and incident workflows
- Prioritizes alerts based on risk, user context, and system sensitivity
In other words, SIEM integration isn’t an administrative chore; it’s the connective tissue of a security ecosystem. Treating SIEM as static storage is like buying a sports car and never starting the engine.
Misconception 2: SIEM Deployment Is Too Complicated to Justify
This perception comes from legacy implementations, where organizations spent months tuning data pipelines, provisioning infrastructure, and building rule sets from scratch. The industry has moved on. Many teams haven’t.
Today’s SIEM platforms are designed to reduce deployment friction and speed up time to value. They offer:
- Accelerated onboarding with native connectors
- Built-in correlation rules mapped to frameworks like MITRE ATT&CK
- Elastic scaling without hardware headaches
- Preconfigured dashboards for SOC visibility
Complexity doesn’t disappear, but it shifts. Instead of infrastructure complexity, the challenge becomes operational discipline: defining data scopes, prioritizing use cases, and aligning alert workflows with business risk.
Teams stuck in the “SIEM is painful” mindset delay decisions, skip training, and ultimately run underpowered deployments that never realize value.
Misconception 3: SIEM Automatically Secures the Organization
A SIEM is not a guardian angel. Turning it on won’t magically detect attackers or interpret ambiguous signals. Many deployments fail because leaders expect out-of-the-box security.
Effective SIEM management requires:
- Determining what normal behavior looks like
- Building custom rules aligned to business processes
- Regularly tuning detections to accommodate new threats and infrastructure changes
- Assigning analysts who understand both security and context
A SIEM without tuning is like an antivirus without signatures: present, but not protective. The misconception of SIEM as a turnkey solution leads to under-resourced SOC teams and low detection maturity.
Misconception 4: SIEM Creates Alert Fatigue
Alert fatigue exists, but SIEM security doesn’t cause it. Poor configuration does.
Security teams drown in noise because they:
- Collect everything instead of collecting purposefully
- Treat vendor rules as universally applicable
- Lack a tiered triage strategy for alert handling
- Fail to tune thresholds or enrich alerts with context
Modern SIEM security tools use behavioral analytics, machine learning, and real-time threat intel to suppress false positives. When deployed correctly, a SIEM reduces noise instead of producing it. Blaming SIEM cybersecurity for alert chaos is like blaming email for spam.
Misconception 5: SIEM Is Too Expensive for Most Organizations
Historical pricing cemented this misconception. Legacy SIEMs demanded heavy capital expenditure, storage planning, and specialists to tune rules. Today, cloud-based subscription models and modular SIEM deployments make enterprise-grade visibility accessible to teams of any size.
The ROI is even more compelling when you consider:
- Reduced breach impact due to early detection
- Automated investigations that free analysts from repetitive tasks
- Eliminated hardware investments
- Continuous vendor-managed content updates
The true cost isn’t the SIEM—it’s operating without one.
Elevate Threat Detection and Response with NetWitness® SIEM
-Correlate data across users, logs, and network for unified visibility.
-Detect advanced threats with AI-driven analytics and behavioral insights.
-Accelerate investigations using automated enrichment and guided workflows.

Misconception 6: SIEM Replaces Security Professionals
Automation is not replacement. It’s leverage.
Security professionals use SIEM tools to:
- Investigate threats and anomalies
- Prioritize incidents with business-aligned risk scoring
- Map attacker paths using correlated events
- Automate containment and remediation steps
- Feed intelligence back into detection logic
Replacing analysts with SIEM creates a blind spot. SIEM supports decision making; it doesn’t eliminate it.
Misconception 7: SIEM Cannot Protect Against Zero-Day Attacks
This myth stems from a misunderstanding of what zero-day threats actually look like. A zero-day isn’t invisible; it’s simply unknown. Attackers still generate signals when they move laterally, escalate privileges, exfiltrate data, or alter system configurations. Those activities leave telemetry behind.
A well-implemented SIEM security can:
- Detect deviations from baseline behaviors
- Correlate unusual user, device, or process activity
- Identify privilege misuse before exploitation is complete
- Surface system anomalies linked to unpatched vulnerabilities
The misconception persists because organizations expect SIEM security to identify the vulnerability itself. SIEM identifies the impact of that vulnerability, often before the payload is fully deployed. In environments where automated threat intelligence and behavioral analytics are active, SIEM becomes one of the most reliable ways to spot zero-day exploitation in progress.
The real issue isn’t SIEM capability; it’s the absence of disciplined tuning, use case libraries, and continuous log centralization.
Misconception 8: All SIEM Alerts Require the Same Level of Attention
This belief is responsible for more operational burnout than any other SIEM misunderstanding. Teams that assume every alert demands equal action create bottlenecks, ignore severity, and eventually overlook critical signals buried in noise.
Alerts don’t matter equally. They never have. Effective SIEM management requires prioritization.
Modern SIEM platforms solve this by:
- Assigning risk scores based on user roles, asset value, and threat context
- Using behavioral analytics to separate benign anomalies from genuine threats
- Automating low-risk alert handling so analysts focus on incidents that matter
- Continuously refining rules to reduce false positives over time
Without prioritization logic, a SIEM becomes a digitized to-do list instead of a security decision engine. Teams that abandon the “every alert is urgent” mindset cut investigation cycles, reduce alert fatigue, and prevent critical threats from slipping through unnoticed.
How Misconceptions Slow Down Security Teams
Misbeliefs create operational debt. When teams underestimate SIEM security, they:
- Delay integrations across infrastructure and cloud services
- Avoid tuning rules because they assume alerts are unavoidable
- Treat SIEM monitoring as compliance reporting instead of detection engineering
- Fail to automate processes that reduce analyst workload
The result is predictable: inefficient SOCs, unresolved alerts, and threats hiding in plain sight.
The Right Way to Think About SIEM
Modern SIEM security is not a passive database. It is:
- A real-time detection system
- A decision engine for security teams
- A bridge between identity, network, and cloud telemetry
- The first responder in incident response workflows
When aligned with business context, SIEM becomes a force multiplier.
Conclusion
SIEM misconceptions persist because organizations cling to outdated experiences. The technology has matured. Architectures have changed. Threat cycles have accelerated. What hasn’t changed is the need for visibility, correlation, and action.
Organizations that revisit their assumptions unlock the real value of SIEM: reducing risk, accelerating investigation, and ensuring security teams operate strategically, not reactively.
The sooner leaders replace myths with operational clarity, the faster SIEM transforms from a misunderstood tool into the engine that drives modern cybersecurity.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are some of the challenges of using SIEM?
Managing data scope, tuning detections, integrating cloud workloads, and operational ownership are the most common obstacles.
2. What are the key challenges with traditional SIEM deployments?
On-prem infrastructure demands, manual correlation, slow scaling, and siloed data pipelines limited traditional SIEM effectiveness.
3. Why do SIEM misconceptions slow down security teams?
They distort expectations, delay rule tuning, and prevent teams from using automation, integrations, and analytics effectively.
4. Can SIEM security scale in modern cloud and hybrid environments?
Yes. Cloud SIEM platforms are designed for elastic scaling, API-driven telemetry, and hybrid architectures.
5. What do security professionals do with SIEM tools?
They investigate incidents, correlate events, automate response workflows, validate threats, and improve organizational security posture.
Choose the Right SIEM with Confidence






