Snapshot Box
Introduction
Ask anyone responsible for keeping industrial systems running, and they’ll tell you operational technology doesn’t get second chances. If a corporate laptop crashes, it’s annoying. If a turbine, pipeline controller, or robotic arm misfires because someone slipped in malware? That’s a headline nobody wants.
That’s why conversations around What is OT Security? have moved from “nice to understand” to “you better know this before your next board briefing.”
OT environments are older, more fragile, and infinitely more consequential than most IT setups. Yet attackers see them as prime targets. According to multiple government advisories released in 2024, OT-focused attacks rose faster than traditional IT-focused ones because disrupting operations still pays better than stealing spreadsheets.
Let’s break down what OT security truly means, why it matters, and how to strengthen it without turning your industrial team against you.
What is OT Security?
OT security is the practice of protecting operational technology – machines, industrial systems, and the physical processes they control – from cyber threats. It ensures that critical operations stay safe, reliable and uninterrupted even when attackers try to disrupt or manipulate them.
In simpler terms, IT protects data. OT protects everything that keeps the real world running. Power. Water. Manufacturing. Transport. All of it.
OT security must account for older systems, 24/7 availability requirements, safety risks, and the growing convergence of IT and OT networks.
Where OT Cybersecurity Applies:
- Industrial Control Systems (ICS)
- SCADA environments
- PLCs, RTUs, HMIs
- Manufacturing floors
- Energy grids
- Building automation
- Transportation systems
- Oil, gas, and chemical plants
These systems were not designed for the modern internet-driven era. Yet here we are.
Why OT Security Matters More Than Ever
Here’s the uncomfortable truth: OT environments used to rely on isolation as their security model. “No internet equals no threats.” It worked until everything needed remote access, telemetry, data sharing, and cloud integrations.
Now, attackers treat OT like the final boss battle. Why? Because:
- Downtime in OT = money. Lots of it.
- Safety impact increases leverage for extortion.
- Legacy devices are notoriously vulnerable.
- OT teams often lack full visibility across their environments.
In 2025, a joint CISA/ENISA advisory noted that over 70% of OT environments now have some degree of IT connectivity. The moment OT joined the broader network, it joined the threat pool.
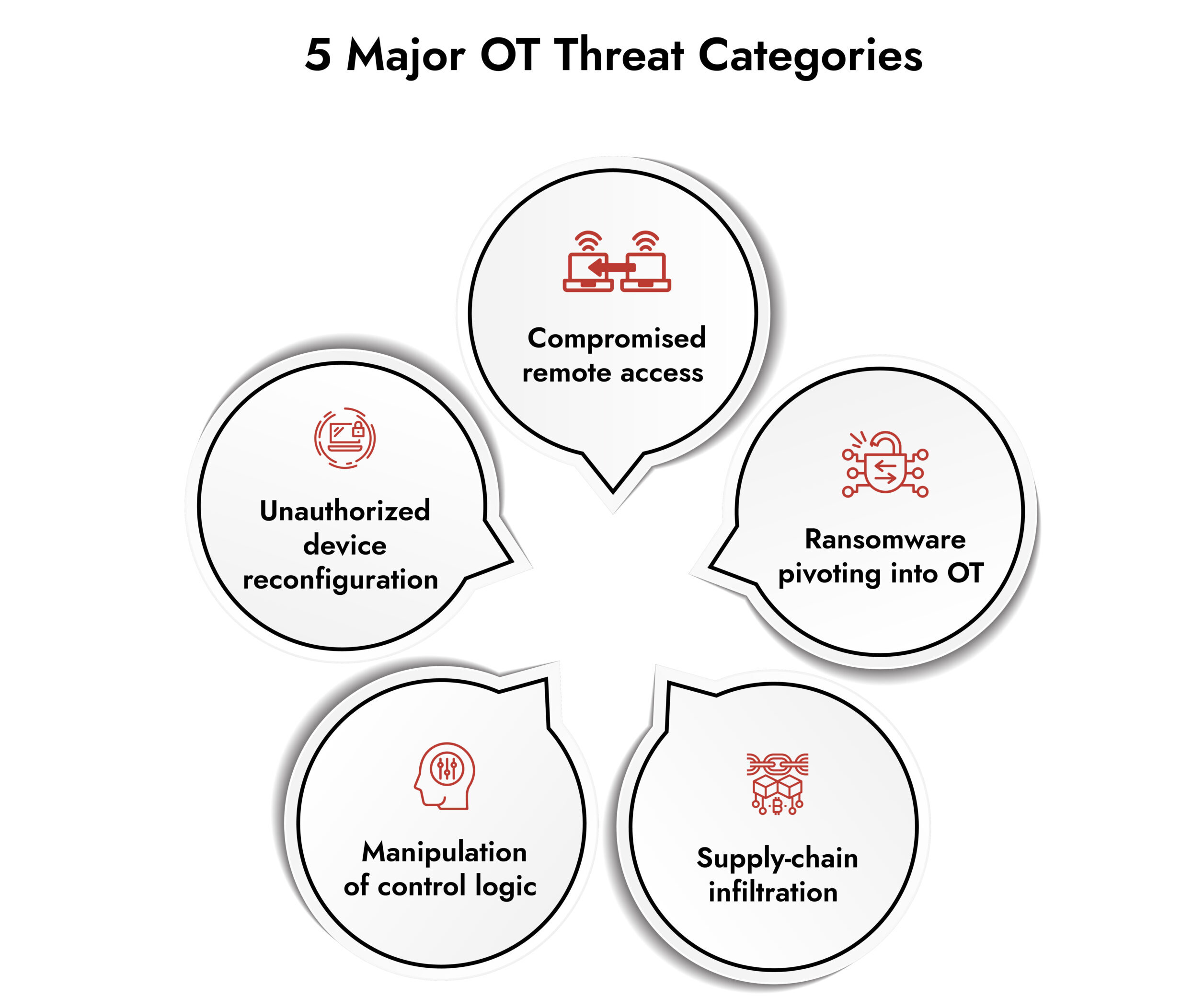
Key Components of Robust OT Cybersecurity
Let’s get straight to the point. Strong operational technology security requires control, visibility, and coordination across layers.
Below are the core pillars.
1. OT Network Visibility
You can’t defend what you can’t see. OT networks often run devices that:
- Don’t speak standard IT protocols
- Don’t generate normal logs
- Don’t respond well to active scanning
Network Visibility must be passive, precise, and continuous. This includes:
- Asset inventory
- Protocol analysis
- Traffic baselining
- Behavior mapping
- Change monitoring
Once you can see everything, you can finally understand what “normal” looks like in your OT world.
2. OT Network Segmentation
Segmentation is your equivalent of building real walls around fragile systems. Strong OT network segmentation isolates critical assets so that:
- Malware can’t hop from IT into OT
- Operator workstations don’t become blast points
- Production lines stay insulated from suspicious traffic
Think of segmentation as crowd control. Everyone stays in their lane, and dangerous behavior gets contained early.
3. Real-Time Threat Detection Built for OT
Real-time threat detection in OT has one job: catch what shouldn’t happen before it becomes a safety or reliability issue. OT threats don’t always look like IT threats.
Examples include:
- Unauthorized PLC logic changes
- Abnormal controller commands
- Strange communication patterns
- Sudden parameter shifts
- Lateral movement into OT from IT
Modern OT cybersecurity solutions blend:
- Packet inspection
- Behavior analytics
- Context-aware alerting
- Protocol-specific analysis
- Machine-level anomaly detection
This isn’t “detecting malware.” It detects deviation from safe operation.

4. Incident Response That Fits OT Reality
Traditional IR playbooks fail in OT because you can’t simply reboot a production line or isolate a controller for mid-shift.
Effective OT incident response requires:
- Coordinated bridges between IT and OT teams
- Deep understanding of process dependencies
- Ability to respond without causing shutdowns
- Evidence-driven root cause analysis
- Controlled remediation steps
It’s part detective work, part engineering, part crisis management.
5. Governance, Compliance, and Safe Engineering Practices
Regulators now expect OT teams to modernize security.
Standards like:
- NIST SP 800-82
- ISA/IEC 62443
- CISA Cross-Sector Cyber Performance Goals
All emphasize secure design, access controls, monitoring, and response capabilities. Governance keeps OT security from being an afterthought. It turns security from a project into a discipline. 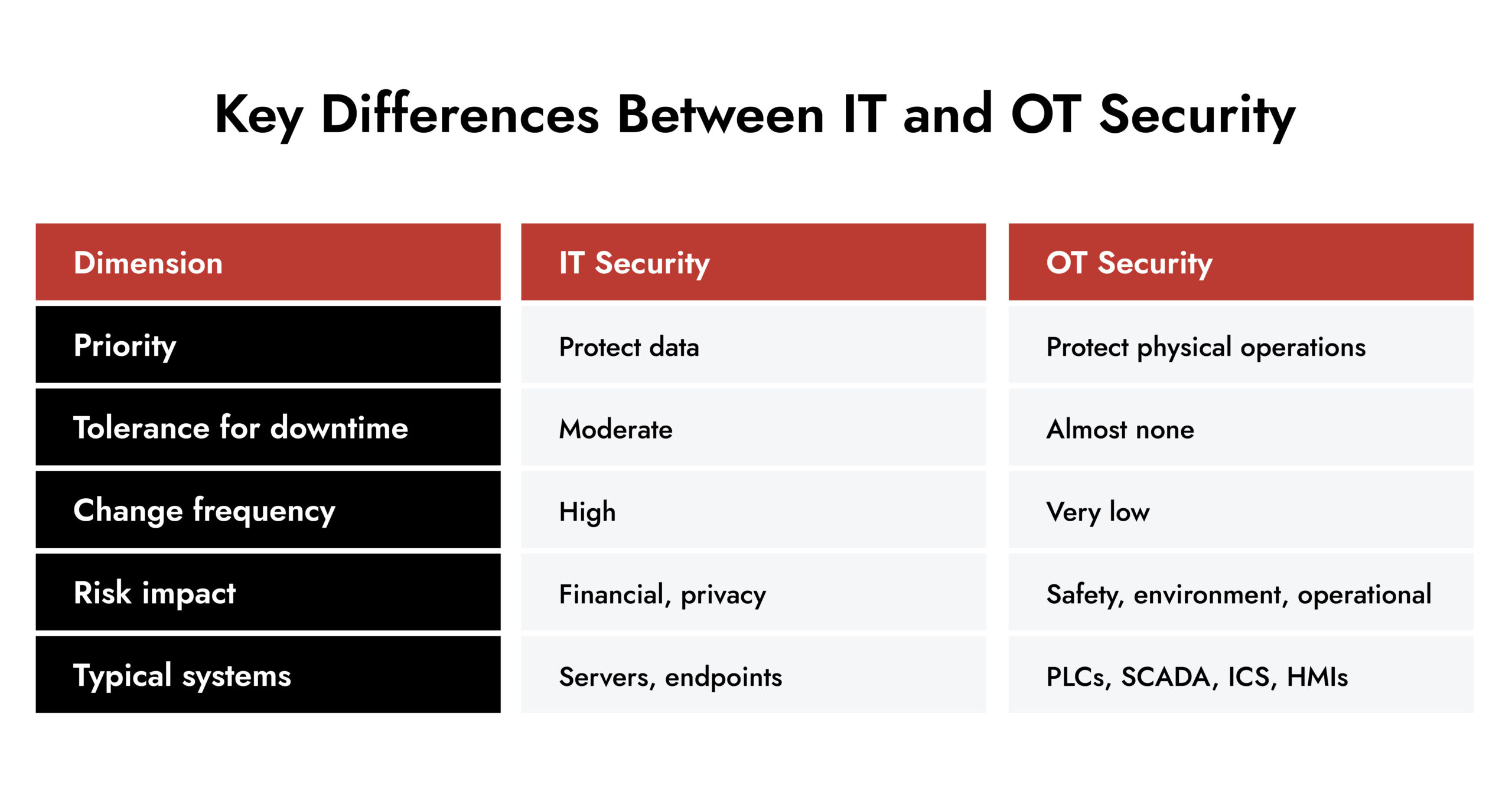
Unmask GenAI Threats — Get Ahead of the Curve

How NetWitness Strengthens OT Cybersecurity
Here’s the thing about OT attacks: they rarely stay in their lane. They start in IT, pivot through unmanaged assets, ride on legacy protocols, and eventually land near your PLCs. This is exactly where most “OT-only” tools fall short, because they only see half the blast radius.
NetWitness approaches OT cybersecurity from the full-stack perspective: network, endpoint, cloud, and industrial traffic – all correlated, all contextualized, all in real-time.
This matters when your SOC needs precision, not guesswork.
Capabilities That Support OT Security:
- Deep Packet Inspection Built for Industrial Reality – NetWitness doesn’t just skim network traffic. It reads raw packets at line speed, including OT-specific protocols like Modbus, DNP3, S7, BACnet, and OPC-UA. That means analysts can see command-level intent – who issued a written command, what changed, and whether anything looks tampered with – without touching or disrupting live systems.
- Full-Stack Visibility Across IT and OT – Most OT attacks don’t walk through the front door; they slip through IT systems, remote access, or identity misuse. NetWitness stitches together telemetry from endpoints, network sensors, cloud logs, and identity systems. The result is a clear view of how an attacker moves from IT into OT, with the historical breadcrumbs to prove it.
- Behavioral Detection That Understands OT Logic – Industrial systems behave in predictable rhythms. When those rhythms break, something’s up. NetWitness uses behavioral analytics to flag the exact kind of anomalies that matter in OT: strange function codes, unusual cyclic traffic, engineering stations acting out of character, or firmware doing things it shouldn’t.
- A Unified Investigation Timeline – OT incidents often require jumping between five different tools. NetWitness eliminates that. Analysts can move from an IT compromise to OT protocol for misuse inside a single interface. Every step of the kill chain – initial access, lateral movement, command manipulation, operational impact – shows up in one cohesive timeline.
- Response Workflows That Respect Operational Constraints – In OT, “just block everything” isn’t an option. NetWitness supports guided and semi-automated response actions designed for environments that can’t go offline. Analysts can isolate a network segment, contain a suspicious session, or stop unauthorized commands – all without freezing production or interfering with safety systems.
- ICS-Aware Threat Intelligence – The platform enriches alerts with OT-specific threat intel. Think MITRE ATT&CK for ICS techniques, known adversary playbooks, protocol exploitation patterns, and industry-specific indicators. This gives security teams the context they need to understand not just what happened, but why it matters for industrial operations.
- Full-Fidelity Forensics When Every Second Counts – After an OT incident, forensic clarity is everything. NetWitness captures full-fidelity packet data, so teams can replay exactly what crossed the wire – who sent which command, how a sequence unfolded, and what impact it had on ICS logic or network behavior. No guessing, no gaps.
In short, NetWitness gives OT teams the depth, visibility, and forensic precision needed when downtime isn’t a line item on a spreadsheet; it’s a real-world operational hit.
Conclusion
OT security isn’t optional anymore. Every industry that relies on physical systems – energy, manufacturing, transportation, healthcare, logistics, now faces adversaries who understand the value of disruption.
With adequate visibility, segmentation, detection and response capabilities, OT environments can be effectively secured. NetWitness offers an opportunity to improve OT security without interfering with business processes by providing early detection of threats, a clear investigation of incidents, and an accurate response to incidents.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is OT Security?
OT Security protects operational technology systems, like industrial control systems from cyber threats. It ensures uptime, safety, and reliability across physical processes.
2. Why is OT Security important?
OT systems run critical operations. A cyberattack on them can cause physical damage, production outages, financial loss, and safety risks. Strong OT cybersecurity reduces exposure and keeps operations stable.
3. What are the key components of OT Security?
Visibility, OT network segmentation, continuous monitoring, real-time detection, strong access controls, and coordinated incident response form the foundation of a robust OT cybersecurity strategy.
4. Which network deception software is best for OT security?
The best tools are those that integrate cleanly into OT environments, avoid introducing operational risk, and support passive, safe deception capabilities. Look for solutions that can blend with existing OT cybersecurity solutions and provide accurate behavioral signals.
5. Who provides the top OT security in networking?
Leading providers combine deep network analytics, behavioral detection, and investigation. Solutions like NetWitness offer comprehensive detection and response capabilities that support converged IT/OT environments.
6. What are the biggest challenges in OT Security?
Aging systems, lack of visibility, IT/OT convergence, limited downtime patching, and specialized protocols all create complexity. OT security must balance operational safety with modern threat detection.
Autonomous AI Defenders for a Smarter SOC






