Staying Ahead of Hidden Threats in Encrypted Data
Encrypted network traffic has been on the rise for years due to a combination of factors, including the growing focus on data privacy and security, adoption of cloud-based services, and changes in how people work and communicate.
But encrypted network traffic also presents unique challenges for threat hunters. By obscuring visibility, encryption makes it more difficult to detect potential threats and calls for advanced network traffic analysis techniques.
In many ways, encrypted network traffic is like Schrödinger’s cat of information security—we think the data is encrypted, and we hope it’s encrypted. Still, we don’t know for sure unless we examine the underlying network traffic. Security analysts must validate that encryption is functioning correctly to ensure data moves safely and securely.
In this context, proactive threat hunting is about identifying risk as much as detecting attackers. While many associate it with “finding the bad guys,” it’s often about discovering misconfigurations—which are far more common than active intrusions.
By understanding the challenges of encrypted network traffic and implementing proactive hunting strategies, organizations can better protect themselves against misconfigurations and cyberattacks that exploit weaknesses in network traffic.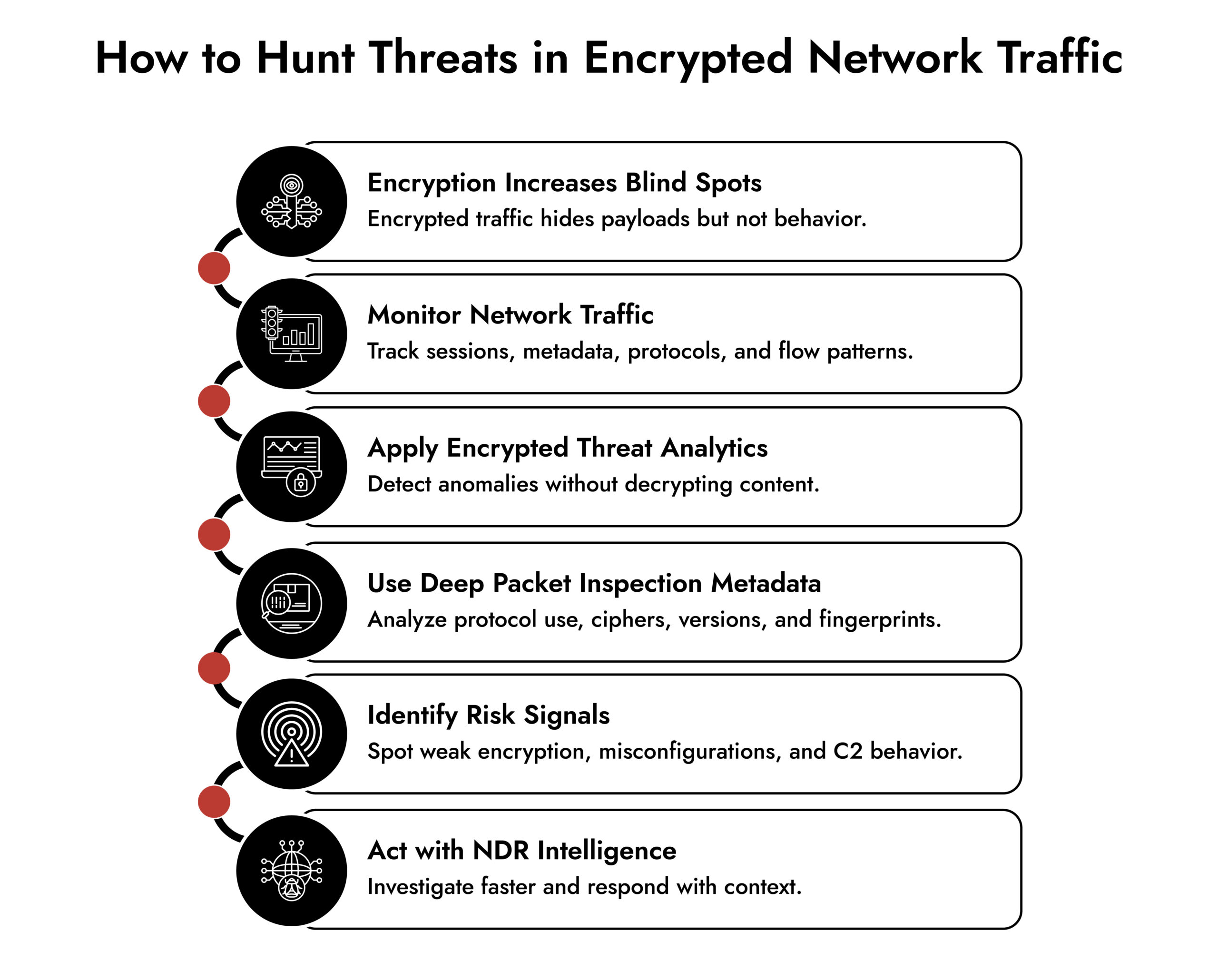
Brief Explanation of Encryption
Encryption converts readable data (plaintext) into unreadable code (ciphertext) during transmission.
The process works like this:
- Data is encrypted before it moves across the network
- The receiver decrypts it using a key
- Anyone in between only sees encrypted traffic
With plaintext traffic, issues are obvious.
With encrypted traffic, visibility drops.
That’s why security teams rely on behavior-based analysis, not payload inspection. Instead of reading content, they analyze patterns, protocols, metadata, and anomalies within network traffic.
Key Benefits of Network Traffic Analysis
Network traffic analysis gives security teams visibility where traditional tools fall short, especially in encrypted environments.
Key benefits include:
- Improved visibility into encrypted traffic
Even when payloads are hidden, analyzing metadata, protocols, and behavior helps teams understand what’s happening on the network.
- Early detection of hidden threats
Abnormal traffic patterns, unusual connections, and suspicious beaconing often surface before alerts trigger elsewhere.
- Faster threat investigation
Network traffic analysis provides context around who communicated with whom, when, and how, reducing investigation time.
- Reduced blind spots across the network
Continuous network traffic monitoring helps uncover unmanaged assets, shadow IT, and misconfigured services.
- Stronger incident response
By analyzing network traffic in real time, teams can contain threats faster and limit lateral movement.
- Better compliance and audit support
Network traffic data helps validate encryption strength, protocol usage, and policy enforcement.
This is why organizations rely on network traffic analysis to move from reactive alerting to proactive security.
Strengthen Network Visibility with NetWitness® Network Traffic Security Assessment
-Uncover hidden threats through deep packet inspection and analytics.
-Identify vulnerabilities and blind spots before they’re exploited.
-Enhance detection and response with NDR-driven intelligence.

Checking Facts and Identifying Risks
Checking facts and identifying risks is all about challenging assumptions—analyzing network traffic to ensure it aligns with what’s expected.
If an organization has policies stating “X, Y, and Z are not allowed,” it might be tempting to assume compliance. However, network traffic monitoring often reveals violations or deviations.
By proactively identifying risks, security teams can confirm whether policies are being followed and reduce exposure to misconfigurations or threats hidden in encrypted network traffic.
Tips for Checking Facts and Identifying Risks
- Start with current policies: Evaluate the current policies and establish the datasets needed to authenticate them, such as network traffic monitoring systems.
- Begin with a theory: Any proactive threat hunt starts with one. Narrow down on what you are searching, and then apply network traffic analysis tools to test your hypothesis and locate anomalies.
- Identify mismatching protocols: Use protocol mismatches to scan network traffic: A protocol mismatch occurs when the network traffic is executed using a protocol that is not anticipated. Certain failures can be innocent malformations, whereas some can signify malicious intent.
- Look at client metakeys: The client metakey shows what the application was used to start the network traffic (through the user-agent field). Protocol mismatch or redirect even with encrypted traffic can provide insight to an investigator.
- Consider the key of the cipher: The cipher key is the algorithm of encryption. Weak, or old algorithms can be a source of vulnerability to encrypted network traffic, and must be checked on a regular basis.
- Think about version key: The version key denotes the cryptographic protocol version (e.g. TLS 1.0). The older protocols may be used against the attacker and it is the best to keep track of old or unauthorized versions.
Supporting Compliance and Audits
As compliance regulations and cyber insurance audits grow more rigorous, organizations must demonstrate how data in network traffic is protected.
This involves assessing encryption strength, protocol versions, and algorithms (ciphers) used in data transmission.
Many organizations ask, “How do we translate this network traffic data into business terms?”
Tips for Supporting Audits
1. Choose a tool with reporting capabilities:
Select a network traffic monitoring platform that translates technical findings into business-ready reports for executives.
2. Translate network traffic data for actionable results:
Break down network traffic insights to show compliance status and help decision-makers shape better security policies.
By connecting technical monitoring with business needs, organizations ensure both compliance and informed governance.
Jittery Robots and C2 Traffic
Command and control (C2) traffic occurs when attackers communicate with compromised systems using network traffic as the medium.
Once a malicious payload executes, it begins “beaconing” back to the command server. Traditionally, such patterns—like beacons every 30 seconds—were easy to identify in plaintext network traffic.
But with encrypted network traffic, attackers have adapted. They now use jitter, introducing randomness in beacon timing or payload size to hide activity.
This makes detection based on predictable patterns ineffective. Modern proactive cloud threat hunting uses baselines and extended observation windows to spot these subtle patterns. Over hours or days, even jittered beacons reveal traces of regularity.
Detecting behavior in encrypted network traffic is often just the first step—an entry point for deeper investigation. Integrating advanced analytics strengthens detection accuracy.
Tips for investigating C2 Network Traffic
- Maintain situational awareness and visibility – Identify blind spots within network traffic and understand how data flows across systems.
- Choose a flexible tool – Ensure your network traffic analysis tool can organize and correlate data according to your team’s workflow.
JA3 and JA3S
JA3 and JA3S are open-source techniques for fingerprinting client and server applications in TLS network traffic.
- JA3 fingerprints the client “hello” message during SSL/TLS handshakes.
- JA3S fingerprints the server’s response.
Together, they form unique hashes for encrypted sessions, allowing analysts to track suspicious connections even when payloads are hidden.
Tips for leveraging JA3 and JA3S
1. Provide hash values as indicators of compromise (IoCs):
Like any other IoC, you can feed JA3 and JA3S hashes into a tool of your choice, tag them, and alert on them. If you leverage JA3/s from a proactive threat hunting intel perspective, make sure you monitor network traffic, maintain, and prune them, just like any other IoC artifact. A SOAR and TIP platform is very useful for the automated curation of IoC artifacts.
2. Baseline JA3 and JA3S:
Set a time window and capture the unique pairs of JA3 and JA3S from network traffic to gather critical servers and alert on new anomalies. JA3S values don’t change as often as JA3 values, so if you combine the hashes, monitor critical servers, and baseline them; anomaly detection will be more high-fidelity.
3. Leverage a user entity and behavior analytics (UEBA) tool:
A UEBA tool can allow organizations to conduct a baseline over a more extended period for more devices by monitoring network traffic. Ultimately, UEBA is all about anomaly detection. An effective UEBA will continue to learn and alert on outliers in the dataset.
How NetWitness can Help
A network detection and response (NDR) platform like NetWitness provides comprehensive visibility for proactive threat hunting in encrypted network traffic.
With NetWitness, organizations can:
- Analyze encrypted traffic to decode concealed threats.
- Anomaly detection Real-time network traffic analysis and machine learning can be used to detect anomalies.
- Explain and present results using dashboards, notifications, and report compliance-ready.
Automate and workflow respondent-driven processes. NetWitness can assist organizations to move beyond the reactive detection to the proactive defense, by integrating network monitoring with intelligent analytics.
Conclusion
Privacy cannot be achieved without encryption and it hides danger. This means that threats are able to pass unnoticed without the visibility of encrypted network traffic.
Organizations can identify an unnoticed activity, justify encryption, and make sure that encrypted traffic does not form a blind spot to the attackers through proactive threat searching, tracking network traffic, and interpretations such as NetWitness NDR.
See Every Threat, Stop Every Attack
Gain complete visibility across cloud, on-prem, and virtual networks with NetWitness® Network Detection and Response. Detect and investigate threats faster with real-time analytics and forensic-grade session reconstruction.





