Key Takeaways
- Signature and rule-based detection both rely on predefined patterns or logic, making them effective at quickly identifying known threats and filtering out routine malware. However, they struggle with anything new, modified, or designed to evade those defined rules.
- Anomaly detection identifies behavior that deviates from normal patterns, making it effective against insider misuse, lateral movement, and stealthy attacks.
- Heuristic detection evaluates what a process is attempting to do, helping identify malicious intent even when the threat has no known signature or rule.
- Threat intelligence adds to a global context, enabling teams to prioritize alerts and detect emerging attacks before they directly target the environment.
Introduction
Security teams talk a lot about tools, dashboards, and tech stacks, but here’s the truth most people skip. None of that matters unless you understand how threats are actually detected in the first place. Bad actors don’t stroll in wearing a label. They blend in. They imitate employees. They sit quietly in network corners, waiting for the right moment.
So, the question is simple. How do you spot something that wants to stay invisible?
You rely on four core approaches. Every threat detection tool in the market, from simple antivirus engines to enterprise grade threat detection and response solutions, builds on these methods. Once you understand them, you start seeing why certain attacks slip through and why some tools outperform others.
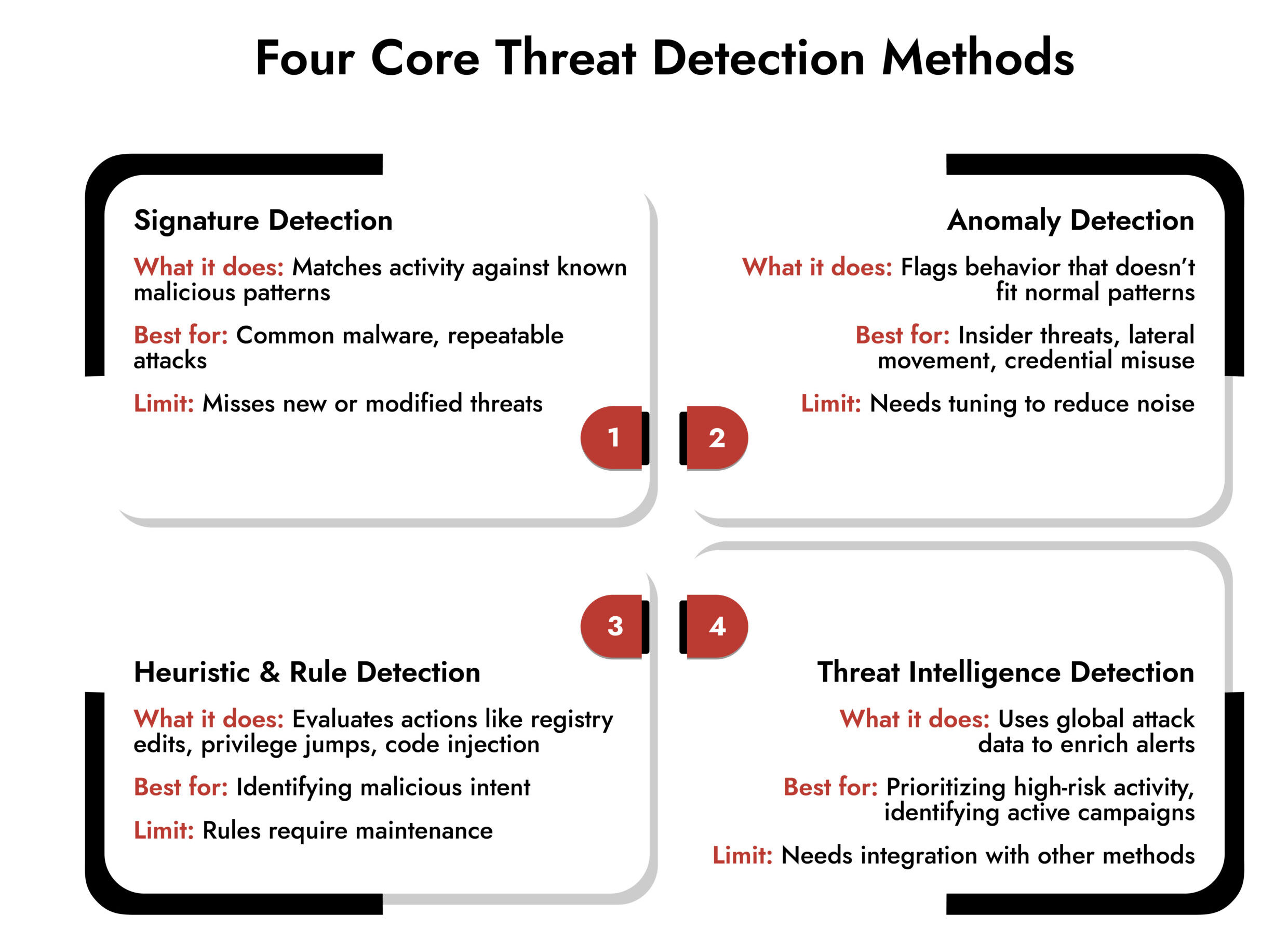
4 Threat Detection Methods Explained
1. Signature Based Detection: The Familiar Face Check
Think of this method like facial recognition at an airport. It works only if it already knows who to look for. Signature based detection compares files, traffic, and processes with known malicious indicators. If there’s a match, the alert fires instantly.
It’s direct. It’s fast. And honestly, it still carries most of the weight for everyday threats. Commodity malware, phishing attachments, old ransomware strains these get caught early because they reuse patterns.
But things get tricky when the attacker changes even a small detail. A new version of the malware appears, or the payload shifts slightly. Suddenly the signature no longer matches. That’s why relying on this method alone is risky. It’s like checking a guest list but letting anyone in if you don’t see their name.
Still, this is a necessary layer of cyber threat detection. It filters out the obvious junk so analysts can focus on the real problems.
2. Anomaly Based Detection: Spotting When Something Just Feels Off
Every environment has patterns. Users log in at certain times. Servers handle predictable traffic. Applications talk to each other in established patterns.
Now imagine one day the pattern changes. A user who always logs in from Mumbai suddenly logs in from another country. A system that usually sends a few megabytes an hour suddenly pushes a hundred times more. These shifts aren’t always attacks, but they’re worth a closer look.
That’s the idea behind anomaly-based detection. Instead of hunting for specific malicious signatures, it watches behavior that doesn’t fit the baseline. This is where cyber security threat detection becomes more like reading body language than checking IDs.
The catch is the learning period. In the early days, the system doesn’t fully understand what “normal” means, so it may flag things that are harmless. Once tuned in, though, this approach becomes incredibly powerful. It spots insider threats, privilege misuse, slow lateral movement, and any attack that tries to sneak quietly.
This method thrives in modern environments where attackers mimic normal activity to avoid being detected. When done right, anomaly detection does not just raise alerts. It guides analysts to moments when something feels off before an incident turns into a mess.
3. Heuristic and Rule Based Detection: Studying the Attacker’s Intent
Signatures tell you what threats look like. Anomalies tell you what looks strange. Heuristics tell you why something might be dangerous.
This method evaluates actions instead of appearances. It studies what a process is trying to do. For instance, is a script editing registry keys? Is a program injecting code into another process? Are files being encrypted across multiple directories at once?
Even if these actions come from a brand new, never seen before strain of malware, heuristic analysis picks up the intent. Pair this with rule-based logic, and the system becomes far more adaptable.
Rules can be simple:
- Multiple failed logins.
- Suspicious privilege escalation.
Or they can be complex:
- A rare authentication anomaly combined with an abnormal outbound connection.
What makes this method so important is the control it gives teams. Analysts can build rules based on how their environment works instead of waiting for vendors to update signatures. Attackers can rewrite malware endlessly, but they can’t avoid performing the core actions needed to break in.
This is one of those methods that grows stronger with time, context, and analyst experience.
4. Threat Intelligence Driven Detection: Bringing in the Outside World
Here’s where everything gets more interesting. Threat intelligence expands your cyber threat detection beyond what’s happening inside your walls. It pulls in data from global attacks, recent campaigns, malicious IPs, domain lists, malware families, and active threat actor behaviors.
Instead of spotting threats only after they hit you, your environment gets early warnings.
For example:
- A new phishing domain starts circulating globally.
- A botnet uses specific command and control servers.
- A ransomware group switches to a new distribution method.
Threat intelligence feeds help your threat detection software adapt quickly because they bring in context your environment alone could never provide.
On its own, intel doesn’t detect threats. It becomes useful only when tied into your other methods. An anomaly becomes more meaningful when matched with known attacker behavior. A suspicious process becomes higher priority if a global campaign uses it. A simple alert becomes urgent if it aligns with a known threat actor technique.
This method turns raw alerts into actionable insight, which is exactly what analysts need when the clock is ticking.
360° Cybersecurity with NetWitness Platform
– Unrivaled visibility into your organization’s data
– Advanced behavioral analytics and threat intelligence
– Threat detections and response actionable with the most complete toolset

Why These Four Methods Work Best Together
Each method has its own strengths. Each one has a gap. But when combined, they cover almost every angle:
- Signature detection handles routine threats.
- Anomaly detection focuses on unexpected behavior.
- Heuristic detection watches for intent.
- Threat intelligence brings clarity and context from the outside world.
Together, they balance accuracy with adaptability. They reduce noise. They shorten investigation time. And most importantly, they help threat detection and response solutions to catch attacks that would otherwise go unnoticed.
Attackers evolve quickly. Blending these methods keeps you a step ahead.
How to Choose Threat Detection Tools That Actually Work
Once you understand the fundamentals, choosing tools becomes a lot more practical. You’re not just buying dashboards. You’re buying the way those tools detect threats.
A strong solution should do three things:
- Combine all four detection methods instead of relying on one.
- Scale with your data and infrastructure.
- Help analysts make decisions faster instead of drowning them in alerts.
If a product can’t deliver on these basics, it’s not built for the threat landscape you’re facing.
Cyber threat detection doesn’t improve by adding more tools. It improves by using tools that think smarter.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are 4 methods of threat detection?
The four primary methods are signature-based detection (comparing against known threat databases), anomaly-based detection (identifying deviations from normal behavior), behavior-based detection (analyzing patterns to identify malicious intent), and threat intelligence-based detection (using external data sources and indicators of compromise).
2. Which threat detection method is most effective?
No single method is most effective on its own. Signature-based detection excels at catching known threats quickly, but struggles with new attacks. Anomaly-based detection catches novel threats but can produce false positives. Behavior-based detection identifies sophisticated attacks but requires advanced analytics. Threat intelligence-based detection provides proactive defense but depends on external data quality. The most effective approach combines all four methods.
3. Why is combining multiple threat detection methods important?
Combining multiple threat detection methods creates defense in depth. Each method has strengths and weaknesses—what one method misses, another catches. Attackers use varied techniques in their campaigns, and a multi-layered approach ensures you can detect threats at different stages. A zero-day exploit might have no signature, but it still creates anomalies and exhibits malicious behavior that other methods can catch.
4. How does behavioral threat detection work?
Behavioral threat detection analyzes patterns of user, application, and system activities to identify malicious intent. It establishes baselines of normal operations and then looks for sequences of actions that indicate threats like privilege escalation, lateral movement, or data exfiltration. Even when individual actions appear legitimate, the pattern and context reveal whether something malicious is happening.
5. How does AI enhance modern threat detection methods?
AI and machine learning enhance threat detection by processing vast amounts of data to identify patterns humans would miss. They establish sophisticated baselines that account for context and time variations, reduce false positives by understanding nuance, and adapt automatically to evolving threats. AI enables automated threat hunting, predictive analysis of attack vectors, and rapid response capabilities that handle complexity beyond human capacity.
Rolling the Dice: Ransomware in the Gaming Industry
Discover how ransomware attacks hit gaming companies, how attackers moved laterally, and why network visibility is key. Learn real-world lessons and strategies to detect, respond, and protect critical systems.





