How does machine learning improve cybersecurity?
Machine learning in cybersecurity allows organizations to detect, analyze, and prioritize threats at scale. Machine learning security systems use behavioral analytics in cybersecurity to understand normal activity and apply machine learning threat detection to spot deviations that signal attacks. Powered by cybersecurity data analytics, these models continuously enhance cybersecurity risk assessment by reducing false positives and focusing attention on the threats that matter most.
Introduction
Cyber threats aren’t what they used to be. Attackers are faster, smarter, and increasingly automated. The old playbook of signature-based detection and manual threat hunting can’t keep up anymore. That’s where machine learning in cybersecurity comes in, and it’s changing the game in ways that matter.
Why Machine Learning in Cybersecurity Matters Now
Here’s the thing: modern networks generate massive amounts of data every second. Logs, traffic patterns, user behaviors, endpoint activities. No human team can process all of that in real time. Machine learning can. It spots patterns in chaos, identifies anomalies that humans would miss, and gets smarter as it goes.
Traditional security tools work like bouncers checking IDs against a list. Machine learning works more like a detective who notices when something feels off, even if they’ve never seen that exact scenario before.
How Machine Learning in Cybersecurity is Actually Being Used
Threat Detection That Learns
Machine learning threat detection systems analyze network traffic and flag suspicious activity based on behavior, not just known signatures. If malware disguises itself as legitimate software but behaves differently, ML can catch it. This matters because attackers constantly evolve their tactics. Zero-day exploits and polymorphic malware slip past traditional defenses, but behavioral analysis spots the underlying patterns.
Behavioral Analytics That Knows Your Users
Behavioral analytics cybersecurity tools build profiles of normal user behavior. When someone who typically accesses five files a day suddenly downloads 5,000, the system notices. When login attempts come from impossible locations within minutes of each other, it flags them. This approach catches insider threats and compromised credentials that signature-based tools miss entirely.
Smarter Risk Assessment
Cybersecurity risk assessment used to be periodic and mostly manual. Now, machine learning security platforms continuously evaluate your attack surface. They prioritize vulnerabilities based on actual exploitability and business impact, not just severity scores. They learn which systems matter most and where attackers are likely to strike.
Data Analytics at Scale
Cybersecurity data analytics powered by ML processes billions of events to find the needle in the haystack. Security information and event management systems (SIEM) now use ML to correlate disparate events, reduce false positives, and surface real threats faster. What used to take analysts hours to investigate now happens in seconds.
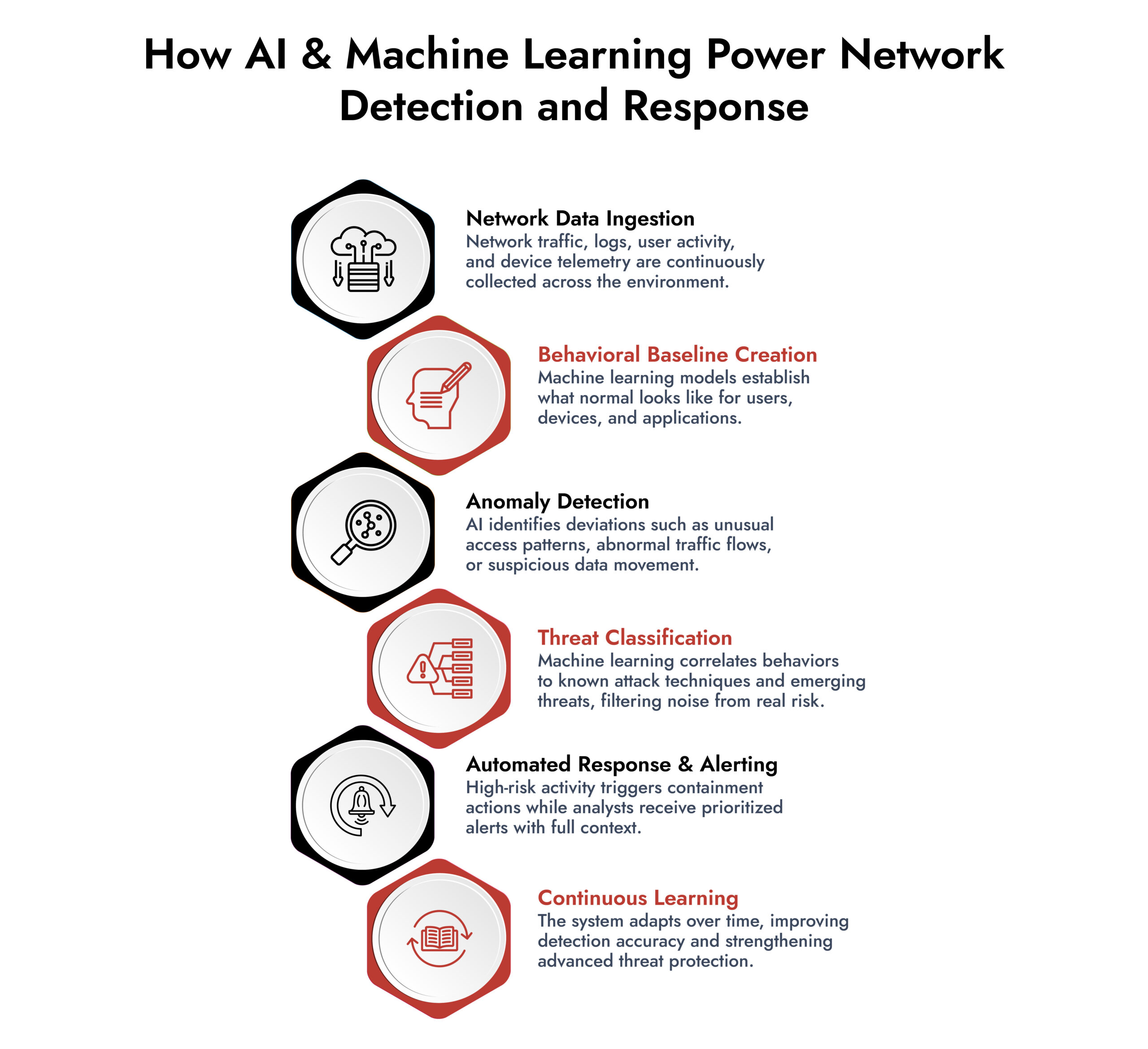
The Machine Learning Models Used in Cybersecurity
Organizations use several types of machine learning in cybersecurity, each with different strengths:
Supervised learning trains on labeled datasets of known threats and benign activity. It’s excellent for detecting variants of known attack patterns. The tradeoff is that it needs quality training data and struggles with completely novel threats.
Unsupervised learning finds patterns without predefined labels. It excels at anomaly detection and discovering unknown threats. The downside is higher false positive rates initially, though these improve over time.
Deep learning uses neural networks to handle complex patterns in large datasets. It’s particularly effective for image-based malware detection, natural language processing of threat intelligence, and analyzing encrypted traffic patterns.
Reinforcement learning adapts through trial and error, making it useful for adaptive security controls that respond to changing attack behaviors in real time.
Unmask GenAI Threats — Get Ahead of the Curve

The Real Risks and Limitations of Machine Learning Security
Machine learning security isn’t perfect, and pretending it is does everyone a disservice.
Adversarial attacks specifically target ML models. Attackers feed carefully crafted inputs designed to fool the system. Think of it as digital camouflage that exploits how the model makes decisions. This is an active area of research, and defenders are still learning how to harden models against these techniques.
Bias in training data leads to blind spots. If your training set doesn’t include certain attack types or underrepresents specific user behaviors, the model won’t detect them well. Worse, it might discriminate against legitimate activities that look unusual simply because they weren’t in the training data.
False positives drain resources. ML systems flag anomalies constantly. If your model isn’t tuned properly, security teams spend all day chasing ghosts instead of real threats. Alert fatigue is real, and it makes organizations less secure, not more.
Model drift happens when the environment changes but the model doesn’t adapt. Networks evolve, new applications get deployed, user behaviors shift. An ML model trained six months ago might be less effective today without retraining.
Black box problem makes some ML decisions hard to explain. When an analyst needs to understand why something was flagged, complex models sometimes can’t provide clear reasoning. This matters for incident response and forensics.
Getting Ready for ML-Driven Security
Organizations that succeed with machine learning in cybersecurity do a few things right:
Start with clean data. Garbage in, garbage out still applies. Before deploying ML tools, audit your data sources. Make sure you’re collecting relevant telemetry and that it’s structured consistently.
Build hybrid teams. You need people who understand both security and data science. That doesn’t mean everyone needs both skillsets, but your teams should work together closely. Security analysts need to understand what the models can and can’t do. Data scientists need to understand the threat landscape.
Establish baselines first. ML works best when it knows what normal looks like. Spend time profiling your environment before turning on automated responses. Let the system learn in monitoring mode initially.
Plan for model maintenance. ML isn’t fire and forget. Schedule regular retraining cycles. Monitor model performance metrics. Be ready to adjust thresholds and retune based on changing conditions.
Keep humans in the loop. This leads to the question everyone asks.
Can Machine Learning Replace Human Analysts?
No. Next question.
Alright, let’s break that down. Machine learning threat detection handles volume and speed that humans can’t match. It processes millions of events, spots subtle patterns, and never gets tired. But it lacks context, creativity, and judgment.
Human analysts understand business logic, organizational politics, and strategic implications. They think like attackers, adapting to novel situations. They make judgment calls in ambiguous situations where the right answer isn’t in any training dataset.
The future isn’t human versus machine. It’s humans augmented by machines. Let ML handle the repetitive analysis, initial triage, and pattern matching. Free your analysts to focus on complex investigations, threat hunting, and strategic security improvements.
The best security operations centers use ML to amplify human capabilities, not replace them. Analysts work faster, make better decisions, and focus on work that actually requires human intelligence.
What Machine Learning Actually Changes for Security Teams
Machine learning in cybersecurity is already here and expanding rapidly. It’s not hype anymore. Organizations using it effectively detect threats faster, respond more accurately, and handle scale that manual processes can’t touch.
But it’s not magic. Success requires investment in data infrastructure, skilled teams, and realistic expectations. The risks are real and need active management. Done right, ML becomes a force multiplier that makes your security program significantly stronger.
The question isn’t whether to adopt machine learning security tools. It’s how quickly you can do it thoughtfully, with proper preparation and realistic expectations about both the benefits and limitations.
The threats are evolving. Your defenses need to evolve faster.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the role of AI and machine learning in threat detection?
AI and machine learning in cybersecurity analyze network behavior at scale to identify anomalies, patterns, and threats in cybersecurity that traditional tools miss. Machine learning threat detection focuses on behavior rather than signatures, improving accuracy against unknown and evolving attacks.
2. What are the two benefits of AI and ML in network monitoring operations?
First, AI-powered network security enables continuous cyber threat monitoring across massive volumes of traffic without human intervention. Second, machine learning reduces false positives by learning what normal activity looks like in a specific environment.
3. How can organizations use AI with networking?
Organizations use AI for network security and monitoring by applying machine learning models to traffic analysis, user behavior analytics, and Network Detection and Response (NDR). This approach enhances cyber threat security by identifying suspicious activity even in complex or segmented environments, including air gap networking.
4. What role does machine learning play in improving NDR accuracy?
Machine learning in NDR improves accuracy by correlating network behavior over time, identifying deviations from baselines, and detecting subtle attack techniques. Instead of relying on static rules, machine learning adapts as the network changes, strengthening AI in network detection and response.
5. How does AI help detect advanced or unknown threats?
AI-powered network security identifies advanced threat protection scenarios by recognizing behavioral patterns associated with malicious activity, even when no known indicators exist. This makes it effective against zero-day attacks, lateral movement, and threats that bypass traditional perimeter defenses.
Autonomous AI Defenders for a Smarter SOC






