Key Takeaways
- Threat detection has shifted from finding known bad to understanding abnormal behavior. AI helps, but it is not the decision-maker.
- Machine learning in cybersecurity improves scale and speed, not certainty. Context and evidence still matter.
- AI-driven threat detection introduces new risks, including blind trust, model drift, and adversarial manipulation.
- Strong enterprise threat detection balances AI insights with analyst control, not automation for its own sake.
- Evidence-based platforms use AI to support investigations, not hide them behind scores.
Introduction
Threat detection used to be about recognition. If the indicator matched, you acted. If it didn’t, you would move on. That model has evolved.
Attackers rotate infrastructure faster than feed updates. Credentials get abused without malware. Encrypted traffic hides intent. By the time a signature appears, the damage is already done. This is why threat detection now leans heavily on AI and machine learning.
But here’s the uncomfortable truth. AI can strengthen threat detection, or it can quietly weaken it. The difference depends on how teams apply it, govern it, and question it.
This article looks at the real role of AI and machine learning in threat detection. Not the promise. Not the pitch. The reality.
Why Traditional Threat Detection Stopped Scaling
Signature-based threat detection still has value. It just cannot fully carry the load as we move into the future of threat detection.
Most modern cybersecurity threats do not announce themselves. They blend in. They reuse legitimate tools. They move laterally and slowly. According to 2024 advisories from CIS (Center for Internet Security) and NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology), the majority of confirmed enterprise breaches bypassed traditional detection methods entirely.
What failed was not technology. It was an assumption.
Threat detection needed a way to spot behavior that felt wrong even when nothing looked obviously malicious. That gap pushed machine learning into cybersecurity into operational use.
What AI and ML Actually Do in Threat Detection
AI does not understand attackers. Machine learning does not understand intent. What they do is identify relationships, deviations, and timing patterns across massive volumes of data.
In practical threat detection systems, machine learning supports four core functions:
- Learning normal behavior across users, systems, and networks
- Flagging anomalies that deviate from learned baselines
- Grouping related activity that would otherwise look isolated
- Prioritizing signals so analysts focus where it matters
Gartner’s 2024 security operation center research made this clear. AI improves detection only when analysts can inspect the evidence behind the alert. When models become opaque, trust collapses.
The Real Benefits of AI-Driven Threat Detection
Used correctly, AI-driven threat detection, in addition to current detection methods, strengthens security operations in very specific ways.
Earlier Visibility into Unknown Activity
Machine learning helps identify behavior that does not match historical patterns. This is especially useful for credential misuse, insider activity, and early-stage lateral movement. It does not prove malicious intent, but it gives teams a head start.
Less Alert Noise
Threat detection fails when analysts drown in low-value alerts. AI helps cluster related events and suppress repetition. This improves focus without hiding in detail.
Better Correlation Across Domains
Modern cybersecurity threat detection spans endpoints, networks, cloud services, and identity systems. Machine learning connects these data sources faster than manual analysis ever could.
Support for Thinly Stretched Teams
The 2025 (ISC)² workforce report shows most organizations still lack experienced analysts. AI helps teams do more with limited capacity, as long as humans stay in control.
Where AI in Cybersecurity Breaks Down
The risks are not theoretical.
Model Drift is Inevitable
The environment change constantly. New applications. New users. New workflows. Machine learning models trained on last quarter’s behavior lose accuracy quietly. Threat detection quality erodes unless teams actively retrain and validate models.
Attackers Adapt to the Model
Adversaries now design campaigns to evade AI-driven threat detection. Government advisories in 2024 documented attempts to poison training data and mimic normal behavior patterns.
Automation Can Outrun Judgment
Automated responses tied to weak confidence scores can disrupt operations faster than attackers. AI should suggest. Humans should decide.
Black Boxes Kill Trust
If analysts cannot explain why something triggered, they hesitate. Investigations slow down. Real threats get dismissed. NIST’s 2024 AI Risk Management Framework warns directly against opaque models in security-critical systems.
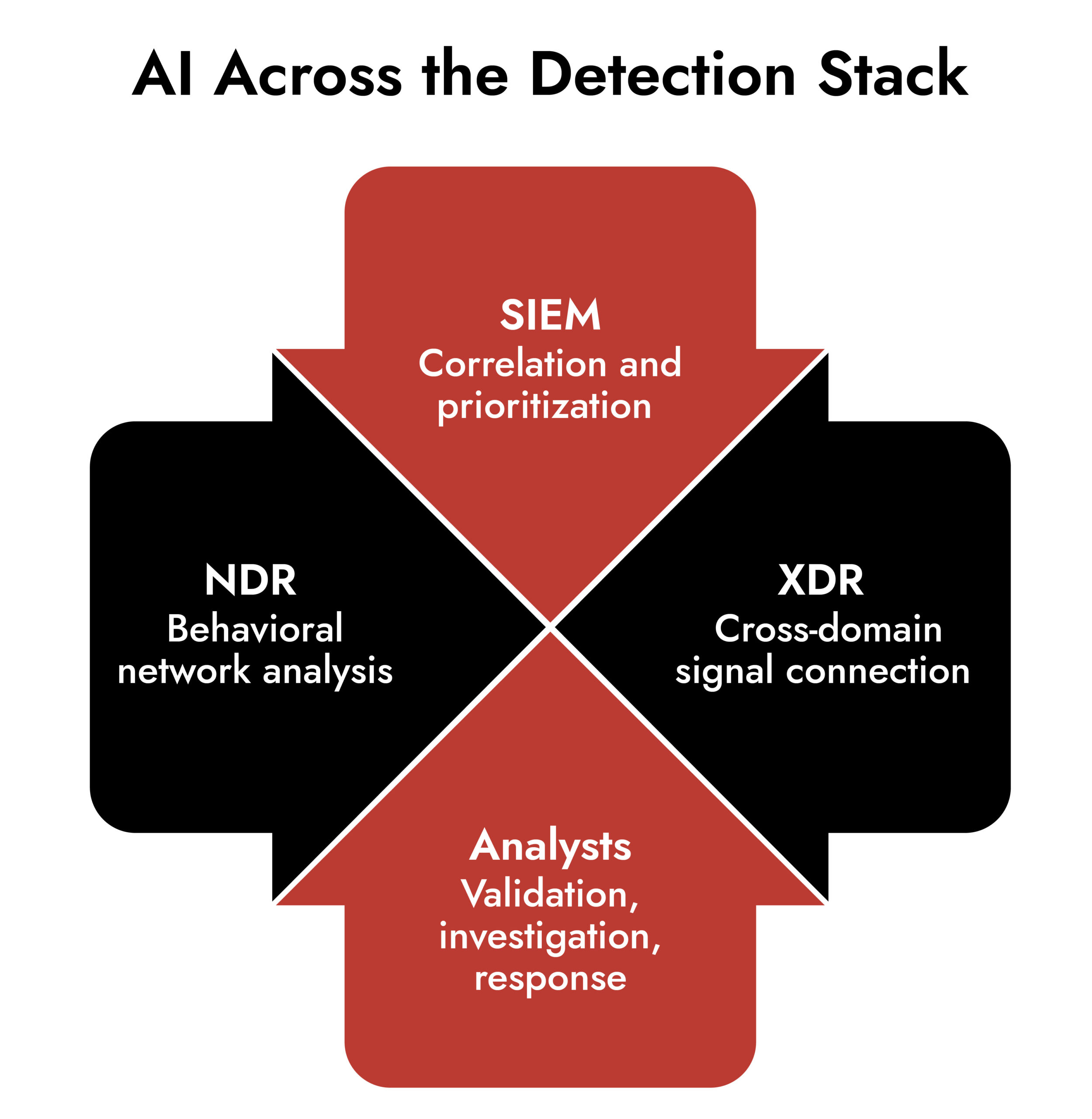
How AI Fits Into SIEM, NDR, and XDR
AI in SIEM
Machine learning improves correlation and reduces noise. It does not fix poor log coverage or inconsistent data. Threat detection still depends on visibility first.
AI in NDR
Network detection and response benefit most when AI highlights abnormal traffic and analysts validate findings with session-level evidence. Without packet context, alerts remain against guesses.
AI in XDR
XDR uses AI to connect activity across endpoints, networks, and identities. Effectiveness depends on integration depth, not the number of models involved.
Gartner’s 2024 research reinforced a simple point. Network telemetry remains the anchor for trustworthy threat detection.
What Responsible AI-Driven Threat Detection Looks Like
AI assists, evidence confirms, humans decide.
Organizations that succeed with AI in cybersecurity follow consistent principles:
- AI supports analysis, not conclusions
- Raw telemetry remains accessible
- Models get validated against real incidents
- Automation stays separate from detection
- Outcomes matter more than alert counts
This approach aligns closely with NIST guidance and current government recommendations on safe AI adoption in security operations.
Unmask GenAI Threats — Get Ahead of the Curve

How NetWitness Supports High-Fidelity Threat Detection
NetWitness approaches threat detection from a different angle. Instead of relying on predictive models or opaque scoring, it focuses on deep visibility, context, and evidence to support confident decision-making.
The platform enables threat detection by capturing and correlating rich telemetry across networks, endpoints, logs, and identities. Analysts can reconstruct sessions, examine artifacts, and trace activity end-to-end without relying on assumptions or probabilistic outputs.
What this really means is simple. Detection is grounded in what actually happened, not what a model predicts might have happened.
This evidence-first approach allows security teams to:
- Validate suspicious activity with full context
- Investigate incidents without blind spots
- Reduce false positives caused by guesswork
- Maintain control over threat detection and response decisions
NetWitness is built for teams that need to understand threats, not just be alerted to them. It supports operational threat detection workflows where human judgment, visibility, and verification remain central.

Conclusion
AI and machine learning now sit at the core of modern threat detection. They help teams see faster, wider, and earlier. They also introduce new failure modes that did not exist before.
The difference between strength and risk comes down to control. Threat detection works best when AI accelerates insight but never replaces accountability. If a system cannot explain what it sees, it cannot defend what matters.
Want to explore how predictive concepts fit into detection operations? Discover how NetWitness approaches early threat detection and operational context.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How are AI and ML used in modern threat detection?
Cybersecurity uses AI and machine learning for the analysis of cyber operations: identifying anomalies based on user behavior (e.g., logging in from different countries), using machine learning algorithms to correlate activities across multiple systems (e.g., a report of unknown logins on multiple devices), and establishing priority for alerts for accelerated threat detection.
2. What are the key benefits of AI-driven threat detection?
Threat detection powered by AI enhances speed, scalability, and visibility, minimizes alert fatigue, and bolsters enterprise threat identification.
3. What risks come with using AI in cybersecurity?
Risks encompass model drift, adversarial evasion, insufficient explainability, excessive automation, and misplaced confidence in AI results.
4. How do attackers evade AI-based threat detection?
Attackers emulate regular behavior, contaminate data, distribute actions gradually, and take advantage of gaps in machine learning models.
5. How is AI used in SIEM, NDR, and XDR platforms?
AI improves correlation in SIEM, behavioral insights in NDR, and cross-domain awareness in XDR, all of which lead to more robust threat detection.
6. Does AI replace human analysts in threat detection?
No. There will not be a complete replacement of human analysts by AI because AI enhances human capabilities in the form of speed of identification. However, human expertise will continue to play an important role in the investigation and resolution process.
Autonomous AI Defenders for a Smarter SOC






